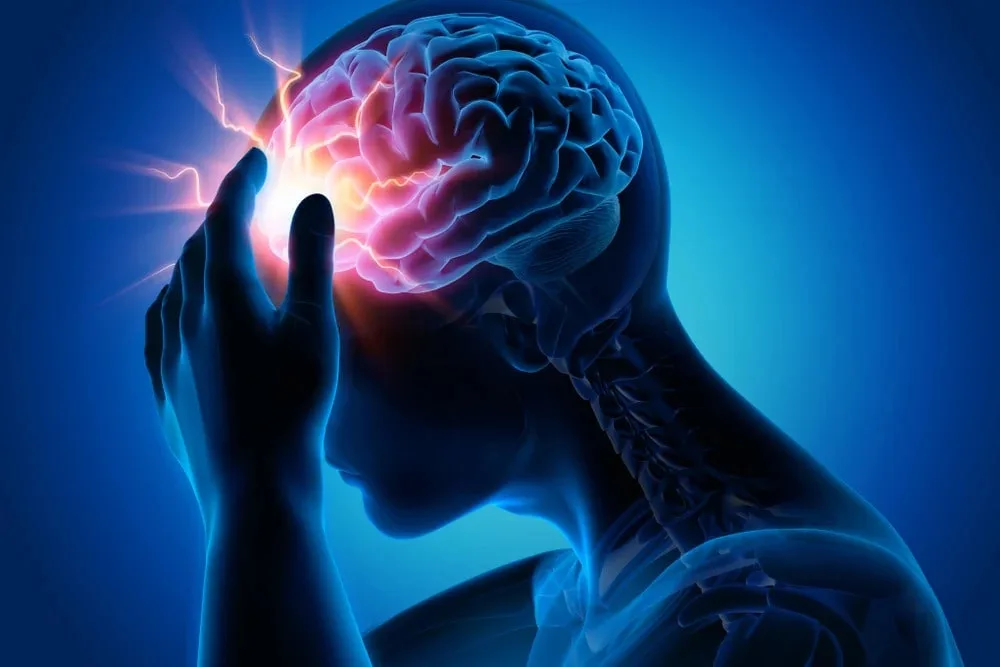
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury caused by a force exerted on the head (such as a bump or a blow) or by a hit to the body that causes the brain to move back and forth inside the skull. This can create both physical and chemical changes in the brain, as well as damage to brain cells.
Concussions are one of the most common types of brain injury, and often occur as a result of playing contact sports or due to motor vehicle accidents. According to recent research from the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI), up to 95% of all emergency department visits for sport-related brain injuries are concussion-related.
What are the symptoms of a concussion?
The signs of a concussion often appear within a few minutes or hours of the head injury. However, sometimes, these symptoms may not be obvious for a few days after sustaining the injury, so it’s important to be vigilant for concussion symptoms for several days after a head injury. Children are especially sensitive to the effects of concussion and are more likely to suffer head injuries than adults.
Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms of a concussion:
- Temporary loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Feeling of pressure inside the head
- Confusion
- Dizziness or blurry vision
- Ringing in the ears
- Amnesia surrounding the traumatic event
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Behaviour and personality changes
How long do concussion symptoms last?
Since each brain injury is different, concussion recovery times also vary based on different factors. Typically, these factors include severity of concussion, age, general state of health before the concussion, and having the necessary resting period after sustaining the concussion.
Most people with mild concussions recover fully, and symptoms can last for days, weeks, or even months. In general, recovery is slower in older individuals. Moreover, individuals who have sustained a concussion in the past may require a longer period to recover from their current head injury.
What is the average recovery time for a concussion?
Concussions are sometimes assigned a grade based on the severity of their symptoms. This classification system also helps to estimate the duration of concussion symptoms.
Grade 0: Headache and difficulty concentrating
Grade 1: Headache, difficulty concentrating, and confusion for less than a minute
Grade 2: Grade 1 symptoms, and a longer period of confusion, that can be accompanied by dizziness, amnesia, ringing in the ears, and irritability
Grade 3: Loss of consciousness for less than a minute
Grade 4: Loss of consciousness for longer than a minute
Typically, following a mild concussion (grade 0 or 1), it is possible to return to a low activity level within a day or two. After a grade 2 concussion, several days of rest with no activity are necessary. Accordingly, a grade 3 or 4 concussion corresponds to a recovery time of several weeks. In all cases of concussion, it is necessary to wait for the symptoms to subside and to avoid returning to work, school or normal activities too quickly.
This is because individuals who suffered a concussion are more susceptible to getting another one, especially if the new injury happens before symptoms from the previous concussion have disappeared.
In fact, one recent scientific study showed that individuals who took the needed break from work and school activities made a full recovery 43 days after sustaining a concussion. However, the individuals who did not wait for their symptoms to disappear before going back to their normal levels of activity made a full recovery at 100 days after the concussion.
Can there be long-term symptoms after a concussion?
Most people make a full recovery after sustaining a concussion, and their symptoms disappear. However, some individuals may experience post-concussion syndrome, which may last for weeks or even months after the concussion.
This is a complex disorder which can include the following symptoms:
- Sensitivity to light and noise
- Irritability
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory problems
- Personality changes
- Sleep disturbances
- Depression
- Disorders of smell and taste
Even after the effects of the initial brain injury have already resolved, having another concussion can have serious negative consequences for brain health. Sustaining multiple concussions over time can even cause long-term neurologic and functional deficits. In addition, repeated concussions can increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease and depression.
Who can develop post-concussion syndrome?
Medical research studies show that the main risk factors include age and sex, with women having a higher risk of developing post-concussion syndrome than men. Moreover, older age is another risk factor to developing post-concussion syndrome. Other identified risk factors include previous brain injury and a medical history of recurring headaches.