Inflammation is the immune system’s natural and vital response to injury and infection. This process is important in healing and repairing damaged tissue, as well as in defending itself against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. Inflammation is broadly categorized into two types: acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation is a short-term inflammatory process that occurs in response to injury, where white blood cells create redness and swelling around the affected area. On the other hand, chronic inflammation is a long-term inflammatory response that can last for several months and even years.
Chronic inflammation can contribute to chronic pain, and is also linked to certain diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and autoimmune disorders, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus. Chronic pain is the result of chronic inflammation, and there is some evidence demonstrating that diet can result in increased systemic inflammation.
5 Foods That Fight Inflammation
Factors such as diet, lifestyle habits and environmental exposures can contribute to chronic inflammation and chronic pain. One of the best ways to prevent inflammation is by choosing the right anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding pro-inflammatory foods.
Here are some of the best foods to incorporate into an anti-inflammatory diet to reduce inflammation and chronic pain:
Berries and citrus fruits
Antioxidants are molecules that are both produced in the body and found in certain foods. These compounds inhibit oxidation, which is a chemical reaction that can produce potentially harmful chemicals called free radicals, leading to chain reactions that may damage the body’s cells. Berries and fruits high in antioxidants include citrus fruit, blueberries, raspberries, goji berries, grapes (red, blue and green varieties).
The benefits of eating a diet rich in natural antioxidants include maintaining the healthy function of the liver, digestive system and kidneys, as well as the prevention of cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
Nuts
Nuts are a superfood that offers a combination of “healthy” fats with protein and complex carbohydrates. In addition, each type of nut provides a unique mix of minerals, fats and phytochemicals. Most nuts contain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which have important anti-inflammatory properties and are essential for many functions and processes in the body.
A recent scientific study has shown that regular consumption of peanuts, tree nuts and walnuts was associated with a significantly lower risk of total cardiovascular disease and coronary heart disease.
Leafy green vegetables
Dark leafy green vegetables, such as broccoli, spinach, beet greens, kale and collard greens, are high in natural antioxidants. Moreover, dark leafy greens are important sources of many essential vitamins (such as vitamins A, C, and K and folate) and minerals (including iron and calcium).
Moreover, they are good sources of fibre. According to research studies, consuming a diet rich in these vegetables can reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease and inflammation.
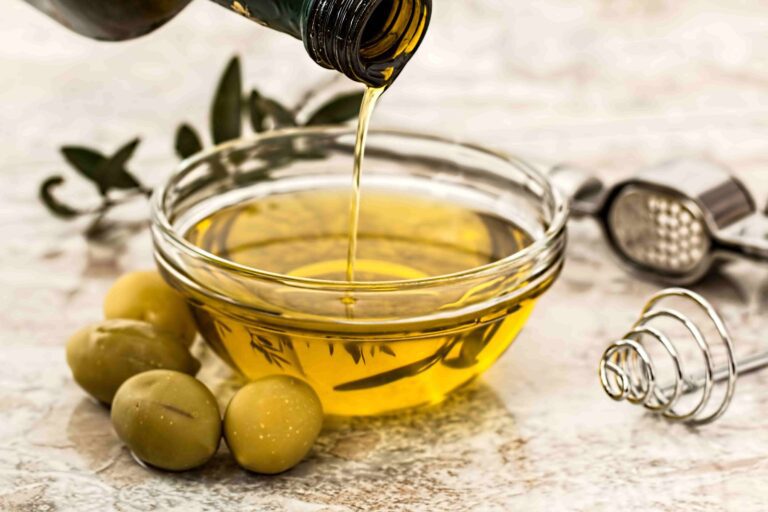
Olive oil
Olive oil has many nutritional benefits and is rich in healthy monounsaturated fat called oleic acid. According to the results of research studies, oleic acid can reduce inflammation and may have some beneficial effects on genes linked to cancer. Moreover, olive oil contains high amounts of vitamins E and K, as well as antioxidant molecules which can help to reduce and prevent inflammation.
It has been shown that oleocanthal, a powerful natural antioxidant contained in olive oil, has similar effects to the anti-inflammatory medication Ibuprofen. Olive oil is an important component of the Mediterranean diet, which can lower the risk of heart disease and early death.
Green tea
Green tea is a great source of antioxidants phytochemicals called polyphenols that can help to fight inflammation and prevent cell damage that can lead to cancer. Tea also contains a molecule called L-theanine (often referred to as theanine), which is a naturally-occurring amino acid that has important neuroprotective effects.
Studies show that green tea has important anti-inflammatory properties, and its natural antioxidants can help to prevent the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension, and even reduce the mortality due to cardiovascular diseases.